The software industry includes many different processes, for example, analysis, development, maintenance, and publication of software. This industry also includes software services, such as training, documentation, and consulting.
Our focus here about the software development life cycle (SDLC). So, due to that different types of projects have different requirements. Therefore, it may be required to choose the SDLC phases according to the specific needs of the project. These different requirements and needs give us various software development approaches to choose from during software implementation.
Types of Software developing life cycles (SDLC)
· Waterfall Model
· V-Shaped Model
· Evolutionary Prototyping Model
· Spiral Method (SDM)
· Iterative and Incremental Methods
· Extreme programming (Agile development)
Waterfall Model
Description
The Waterfall Model is a linear sequential flow. In which progress is seen as flowing steadily downwards (like a waterfall) through the phases of software implementation. This means that any phase in the development process begins only if the previous phase is complete. The waterfall approach does not define the process to go back to the previous phase to handle changes in requirements. The waterfall approach is the earliest approach that was used for software development.
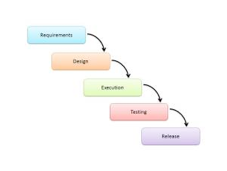
The usage
Projects did not focus on changing requirements, for example, responses to requests for proposals (RFPs)
Advantages and Disadvantages
· Easy to explain to the user· Structures approach.· Stages and activities are well defined· Helps to plan and schedule the project· Verification at each stage ensures early detection of errors/misunderstanding · Each phase has specific deliverables
· Assumes that the requirements of a system can be frozen· Very difficult to go back to any stage after it is finished.· Little flexibility and adjusting scope is difficult and expensive.· Costly and required more time, in addition to a detailed plan
V-Shaped Model
Description
It is an extension of the waterfall model, Instead of moving down linearly, the process steps are bent upwards after the coding phase, to form the typical V shape. The major difference between the v-shaped model and the waterfall model is the early test planning in the v-shaped model.
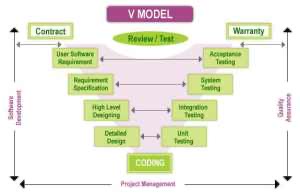
The usage
· Software requirements are clearly defined and known
· Software development technologies and tools are well-known
Advantages and Disadvantages
· Simple and easy to use.· Each phase has specific deliverables.· Higher chance of success over the waterfall model due to the development of test plans early on during the life cycle.· Works well where requirements are easily understood.
· Very inflexible, like the waterfall model.
· Little flexibility and adjusting scope is difficult and expensive.· Software is developed during the implementation phase, so no early prototypes of the software are produced.· Model doesn’t provide a clear path for problems found during testing phases.· Costly and required more time, in addition to a detailed plan
Evolutionary Prototyping Model
Description
It refers to the activity of creating prototypes of software applications, for example, incomplete versions of the software program being developed. It is an activity that can occur in software development. It is used to visualize some components of the software to limit the gap of misunderstanding the customer requirements by the development team. This also will reduce the iterations that may occur in the waterfall approach and hard to be implemented due to the inflexibility of the waterfall approach. So, when the final prototype is developed, the requirement is considered to be frozen.
It has some types, such as:
· Throwaway prototyping: Prototypes that are eventually discarded rather than becoming a part of the finally delivered software
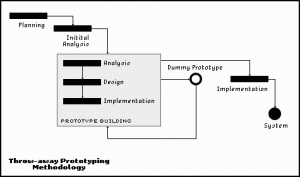
· Evolutionary prototyping: prototypes that evolve into the final system through iterative incorporation of user feedback.
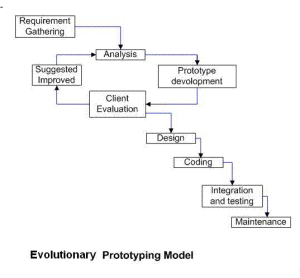
· Incremental prototyping: The final product is built as separate prototypes. In the end, the separate prototypes are merged into an overall design.
· Extreme prototyping: used in web applications mainly. It breaks down web development into three phases, each one based on the preceding one. The first phase is a static prototype that consists mainly of HTML pages. In the second phase, the screens are programmed and fully functional using a simulated services layer. In the third phase, the services are implemented
The usage
This process can be used with any software developing life cycle model. While this shall be focused on systems that need more user interactions. So, the system does not have user interactions, such as, the system does some calculations shall not have prototypes.
Advantages and Disadvantages
· Reduced time and costs, but this can be a disadvantage if the developer loses time in developing the prototypes· Improved and increased user involvement
· Insufficient analysis· User confusion of prototype and finished system· Developer misunderstanding of user objectives· Excessive development time of the prototype· Expense of implementing prototyping
Spiral Method (SDM)
Description
It is combining elements of both design and prototyping-in-stages, to combine the advantages of top-down and bottom-up concepts. This model of development combines the features of the prototyping model and the waterfall model. The spiral model is favored for large, expensive, and complicated projects. This model uses many of the same phases as the waterfall model, in essentially the same order, separated by planning, risk assessment, and the building of prototypes and simulations.
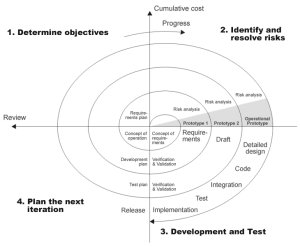
The usage
It is used in shrink-wrap applications and large systems which built-in small phases or segments.
Advantages and Disadvantages
· Estimates (i.e. budget, schedule, etc.) become more realistic as work progresses because important issues are discovered earlier.· Early involvement of developers· Manages risks and develops system into phases
· High cost and time to reach the final product.· Needs special skills to evaluate the risks and assumptions· Highly customized limiting re-usability
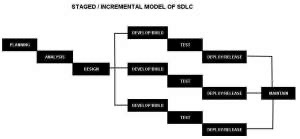
Iterative and Incremental Methods
Description
It is developed to overcome the weaknesses of the waterfall model. It starts with initial planning and ends with deployment with the cyclic interactions in between. The basic idea behind this method is to develop a system through repeated cycles (iterative) and in smaller portions at a time (incremental), allowing software developers to take advantage of what was learned during the development of earlier parts or versions of the system.
It consists of mini waterfalls
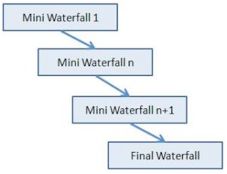
The usage
It is used in shrink-wrap applications and large systems which built-in small phases or segments. Also can be used in a system that has separated components, for example, an ERP system. We can start with the budget module as the first iteration and then we can start with the inventory module and so forth.
Advantages and Disadvantages
· Produces business value early in the development life cycle· Better use of scarce resources through proper increment definition· Can accommodate some change requests between increments· More focused on customer value than the linear approaches· Problems can be detected earlier
· Requires heavy documentation· Follows a defined set of processes· Defines increments based on function and feature dependencies· Requires more customer involvement than the linear approaches· Partitioning the functions and features might be problematic· Integration between iterations can be an issue if this is not considered during the development.
Extreme programming (Agile development)
Description
It is based on iterative and incremental development, where requirements and solutions evolve through collaboration between cross-functional teams.
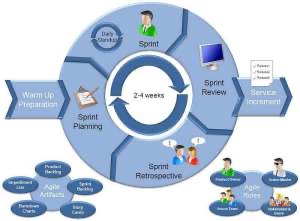
The usage
It can be used with any type of project, but it needs more involvement from customers and is interactive. Also, it can be used when the customer needs to have some functional requirement ready in less than three weeks.
Advantages and Disadvantages
· Decrease the time required to avail some system features.· Face to face communication and continuous inputs from customer representative leaves no space for guesswork.· The result is high-quality software in the least possible time duration and a satisfied customer
· Scalability· Skill of the software developers· Ability of customer to express user needs· Documentation is done at later stages· Reduce the usability of components.· Needs special skills for the team.